Vaccines Aide-mémoire
- Influenza
- Influvac
- IM / deep SC
- 6 to 35 months: 0.25 to 0.5 ml
- All others: 0.5 ml
- Influvac Tetra
- Fluarix Tetra
- Vaxigrip Tetra
- SKYcellflu quadrivalent
- 6 months to < 5 years
- 5 years to < 65 years
- Chronic heart or lung diseases, including asthma
- On follow-up or was admitted for chronic metabolic (including DM), renal, neurologic, hepatic, or hematologic disorders, or immunocompromised
- Aged 18 and below and on long-term aspirin therapy (and therefore at risk of Reye syndrome after influenza infection)
- Pregnancy at any stage
- On ILTC services
- 65 years and older
- MOH circular: hypertension, dyslipidaemia, and pre-diabetes are NOT part of indications
- 6 months to < 9 years
- 2 doses 4 weeks apart if receiving influenza for first time
- All others
- 1 dose annually or every season
- Influenza seasons
- Northern hemisphere - October to March
- Southern hemisphere - April to September
- See MOH circular for specific strains
- SVL
- Trivalent
- Quadrivalent
- Influvac Tetra
- Fluarix Tetra
- Vaxigrip Tetra
- SKYCellflu
- PCV 10 / 13
- (Pneumococcal conjugate)
- PCV10 is only for children up to 5 years old
- Prevenar 13
- Synflorix (PCV10)
- 6 weeks to < 5 years
- 5 years to < 6 years
- Chronic pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, or liver disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cochlear implant or CSF leak
- Anatomic or functional asplenia
- Immunocompromised
- 6 years to < 65 years
- Cochlear implant or CSF leak
- Anatomic or functional asplenia
- Immunocompromised
- 65 years and older
- 1-3 doses in lifetime, depending on age when first dose is given and indication
- NCIS routine schedule
- 3 doses (at ages 4, 6, and 12 months)
- “Children who did not receive PCV as per routine schedule are recommended to receive age- or indication-appropriate doses”
- All others (by age/indication)
- < 1 year
- 2 doses, 8 weeks apart
- 1 booster at 1 year old, at least 8 weeks after D2
- 1 year to < 2 years
- 2 years to < 5 years
- Healthy: 1 dose
- Chronic disease / DM / cochlear implant / CSF leak: 1 dose (MOH) / 2 doses, 8 weeks apart (ACIP)
- Anatomic or functional asplenia / immunocompromised: 2 doses, 8 weeks apart
- 5 years to < 6 years
- Chronic disease / DM / cochlear implant / CSF leak: 1 dose (MOH) / 2 doses, 8 weeks apart (ACIP)
- Anatomic or functional asplenia / immunocompromised: 2 doses, 8 weeks apart
- 6 years and older
- 1 dose regardless of indication
- No need to repeat if completed in childhood
- No need to repeat at > 65 years if already done at < 65 years
- SVL
- Prevenar 13
- Synflorix (PCV10) only for children
- PCV 20
- (Pneumococcal conjugate)
- Prevenar 20
- 18 years to < 65 years
- Chronic pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, or liver disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cochlear implant or CSF leak
- Anatomic or functional asplenia
- Immunocompromised
- 65 years and older
- 1 dose in lifetime, under NAIS
- No need to follow with PPSV23
- Can be used to complete any PCV/PPSV series previously started
- No recommendation under NCIS yet
- Interval after previous PCV/PPSV (by age/comorbidities)
- All aged 65 years or older
- 1 year if either PCV13 or PPSV23 previously
- 5 years if BOTH PCV13 and PPSV23 previously
- 18-64 years with DM or chronic pulmonary, cardiovascular, liver diseases
- 18-64 years with CSF leak or cochlear implant
- 1 year if either PCV13 or PPSV23 previously
- 5 years if BOTH PCV13 and PPSV23 previously
- 18-64 years with CKD or immunocompromise
- 1 year if either PCV13 or PPSV23 previously
- 5 years if BOTH PCV13 and PPSV23 previously
- PPSV 23
- (Pneumococcal polysaccharide)
- Pneumovax 23
- 2 years to < 65 years
- Chronic pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, or liver disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cochlear implant or CSF leak
- Anatomic or functional asplenia
- Immunocompromised
- 65 years and older
- 1-3 doses in lifetime, depending on age and indication
- Healthy
- 1 dose at or after age 65 (1 year after PCV13)
- To give even if given before age 65 (space apart by 5 years)
- Chronic pulmonary, cardiovascular, renal, liver disease, or DM
- 1 dose when age 2 years to < 65 years (8 weeks after PCV13)
- 1 more dose at or after age 65 (1 year after PCV13 and 5 years after PPSV23)
- CSF leak, cochlear implant
- 1 dose when age 2 years to < 65 years (8 weeks after PCV13)
- 1 more dose at or after age 65 (8 weeks after PCV13, 5 years after PPSV23)
- Anatomic or functional asplenia, immunocompromised
- 2 doses, 5 years apart, when age 2 years to < 65 years (8 weeks after PCV13)
- 1 more dose at or after age 65 (8 weeks after PCV13, 5 years after PPSV23)
- Hepatitis A
- Havrix
- IM
- 1 to 18 yo: 0.5 ml
- 19 yo and older: 1 ml
- Vaqta
- IM
- 1 to 17 yo: 0.5 ml
- 18 yo and older: 1 ml
- Avaxim
- IM
- 16 yo and older: 0.5 ml
- 1 year and older*
- Travellers
- Occupational exposure to Hepatitis A (e.g. lab)
- Underlying liver disease
- Awaiting or received liver transplant
- Immunocompromised
- Rationale: at high risk of complications or exposure
- * Use Havrix or Vaqta in paediatric population because Avaxim is only approved for 16 yo and above
- 2 doses
- No need for booster
- >97% remained positive for anti-HAV after 20 years
- Twinrix (Hep A+B) can also be used for Hep A vaccination (only for 18 yo and above)
- Hepatitis B
- Engerix-B
- IM
- 1 to 19 yo: 0.5 ml
- 20 yo and older: 1 ml
- 20 yo and older and on haemodialysis: 2 ml
- Twinrix
- IM
- 18 yo and older: 1 ml
- Not used for < 18 yo
- Part of 6-in-1 (NCIS only)
- From birth
- NAIS: “for persons without evidence of immunity or prior disease”
- NCIS
- Routine schedule
- 3 doses: at birth (Hep B), 2 months (6-in-1), 6 months (6-in-1)
- Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers
- 3 doses: at birth (Hep B), 1 month (Hep B), 6 months (6-in-1)
- General population
- 3 doses: 0, 1, 6 months
- Recheck Hep B status 1 to 2 months after final dose
- Haemodialysis
- 4 doses: 0, 1, 2, 6 months
- Double dose of Engerix-B (2 ml) each time
- Recheck Hep B status 1 to 2 months after final dose
- Check anti-HBS annually: 1 booster dose if anti-HBS < 10 mIU/ml
- Human Papilloma Virus
- (HPV)
- Cervarix / Gardasil / Gardasil-9
- Gardasil (HPV4) no longer available in SG
- 9 years to 45 years
- Universal
- Applicable to both males and females
- PI-approved upper age limits
- Cervarix (HPV2) — till 25 years
- Gardasil (HPV4) — till 26 years
- Gardasil-9 (HPV9) — till 45 years
- NAIS: “If HPV vaccination [implied as HPV2 and HPV4] is initiated but not completed by age 26 years or earlier, remaining dose(s) may be completed after age 26 years, as early as possible, but up to age 45 years”
- - MOH Circular (13 July 2020)
- Protection rates
- Cervarix (HPV2) — 70%
- Gardasil (HPV4) — 70% + genital warts
- Gardasil-9 (HPV9) — 90% + genital warts
- Number of doses (2 or 3) needed is determined by age when first dose is given
- Cervarix (HPV2)
- 9 to 13 years
- 14 to 25 years
- Gardasil (HPV4)
- 9 to 13 years
- 14 to 26 years
- Gardasil-9 (HPV9)
- 9 to 14 years
- 15 to 45 years
- Switching between brands
- No clear guidance from ACIP/SIDS
- HPV9 may be used to continue or complete a series started with HPV2 or HPV4
- Protection against HPV type 16 and 18 unaffected. But efficacy against other strains not studied
- SVL
- Cervarix
- Only subsidised for females
- MMR
- (Measles + Mumps + Rubella)
- M-M-R II (LIVE)
- Priorix (LIVE)
- M-M-R II and Priorix can be used interchangeably (ACIP MMWR 2022)
- 1 year and older
- FDW working in households with a child < 7 years old without documented proof of immunity:
- 2 doses of measles vaccine at least 28 days apart
- Serological evidence of immunity
- Laboratory confirmation of past infection
- Exempted if all children < 7 years old in the household are already fully vaccinated
- NAIS: “for persons without evidence of immunity or prior disease”
- Post-exposure prophylaxis
- To give within 72 hours of exposure to measles if unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated
- No evidence if exposure was to mumps or rubella
- NCIS routine schedule
- 2 doses (12 months, 15 months)
- Dose 1: separate MMR and V ^
- Dose 2: combined MMRV
- 12-week interval between MMR doses here is to harmonise with minimum interval between varicella doses
- All others (including NCIS catch-up)
- 2 doses, 4 weeks apart
- If 1 dose was already given in childhood, only need 1 more dose
- Varicella
- Varivax (LIVE)
- Varilrix (LIVE)
- 1 year and older
- NAIS: “for persons without evidence of immunity or prior disease”
- Post-exposure prophylaxis
- Evidence in unvaccinated children if given within 3-5 days of exposure: reduce incidence and severity of disease
- No evidence for adults
- No evidence for giving second dose if one dose has already been given
- But practically, to give if unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated
- NCIS routine schedule
- 2 doses (12 months, 15 months)
- Dose 1: separate MMR and V ^
- Dose 2: combined MMRV
- 12-week interval between MMR doses here is to harmonise with minimum interval between varicella doses
- Varicella alone
- 2 doses
- 1 to 12 years: 12 weeks apart
- 13 years and older: 4-8 weeks apart
- HCP vaccination
- 2 doses, 4 weeks apart
- DO NOT check varicella antibody levels after vaccine (most commercially available tests are sensitive enough to detect only infection-induced antibodies, and not vaccine-induced antibodies)
- If 1 dose given previously (even if distantly), only 1 more dose needed to complete schedule
- MMR + Varicella
- (MMRV)
- ProQuad (LIVE)
- Priorix-Tetra (LIVE)
- 1 year to 12 years
- Not for use from 13 years and older
- NCIS routine schedule
- 2 doses (12 months, 15 months)
- Dose 1: separate MMR and V ^
- Dose 2: combined MMRV
- Catch-up vaccination
- 2 doses (0, 3 months)
- MMRV can be given as first dose only from age 4 years ^
- Zoster
- Shingrix
- Zostavax (LIVE)
- Zostavax no longer available in SG
- 18 years and older
- With immunocompromising conditions
- 60 years and older
- Shingrix
- Effectiveness against zoster > 90%
- Effectiveness against PHN 70-100%
- Zostavax
- Effectiveness against zoster ~ 50%
- Effectiveness against PHN ~ 65%
- Shingrix
- 2 doses
- Healthy: 2-6 months apart
- Immunocompromised: 1-2 months apart
- Previous Zostavax
- Full 2 doses, after an interval from Zostavax
- Previous zoster
- Full 2 doses, to give after recovery from acute illness (no specific interval recommended)
- No varicella before
- Routine varicella serology testing before vaccination is NOT recommended
- But if serology is confirmed negative, to give varicella vaccination instead
- Zoster can arise from live attenuated virus in varicella vaccine, but not enough evidence to recommend zoster vaccination after previous varicella vaccination
- Zostavax
- 1 dose
- SVL
- Shingrix
- NOT free for HSG
- Tetanus
- Tetavax (TT)
- Imovax d.T. (Td)
- 6 weeks and older
- Formulation used depends on age
- 6 weeks to 6 years: DTaP (5-in-1 / 6-in-1)
- 7 years and above: Tdap / Td / TT
- TT is used only for wound prophylaxis
- Routine vaccination
- NCIS schedule
- Primary series: 3 doses (2, 4, 6 months old)
- Boosters: 2 doses (18 months, 10-11 years old)
- Use DTaP (5-in-1 / 6-in-1) for all doses except for 2nd booster (Tdap)
- 7 years and above
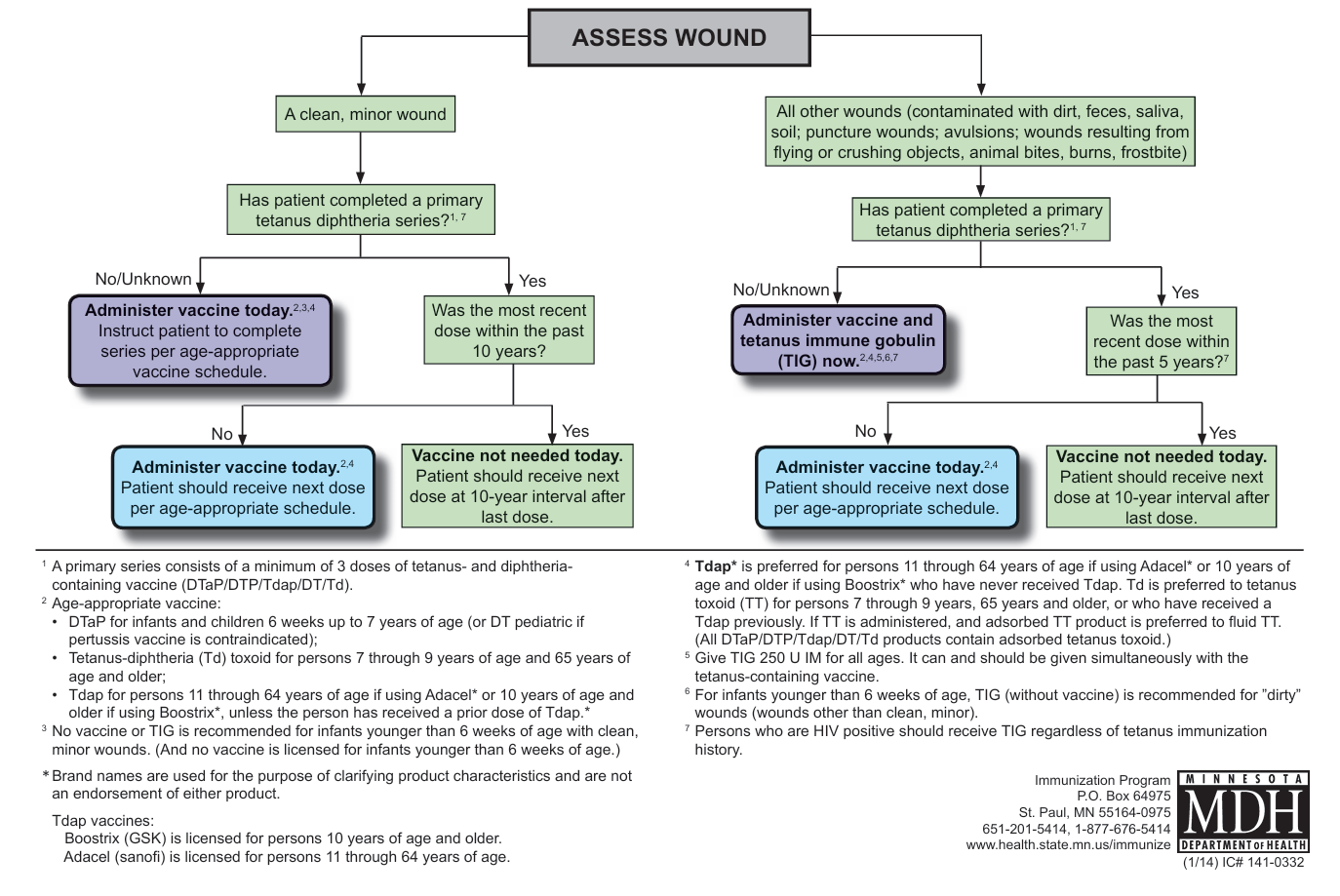
- Post-exposure prophylaxis
- Completed primary series (at least 3 doses)
- Clean, minor wound: 1 dose if last > 10 years ago
- All other wounds: 1 dose if last > 5 years ago
- Incomplete / unknown primary series
- Clean, minor wound: 1 dose now, complete age-appropriate series subsequently
- All other wounds: give Tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) concurrently with tetanus vaccine
- Tdap
- Boostrix
- Adacel
- Boostagen
- IM
- 0.5 ml
- Used ONLY as booster
- 7 years and older
- 6 years and below should use DTaP
- NAIS: During every pregnancy
- ACIP / SIDS
- Not had at least 3 doses of tetanus/diphtheria vaccines previously
- Not had at least 1 dose of Tdap previously
- Due for 10-yearly tetanus/diphtheria booster (Tdap can be used in place of Td)
- Pregnancy
- 1 dose
- Between 16 and 32 weeks (NAIS / SIDS) / 27 and 36 weeks (ACIP) of pregnancy
- Repeat for each pregnancy
- If not given during pregnancy, to give immediately postpartum
- No minimum interval between doses
- Rationale
- Provide newborn with maternal antibodies against pertussis
- Maternal antibodies wane quickly -- vaccinating too early in pregnancy may not be effective
- Some evidence that vaccinating earlier (27 to 32 weeks) may improve amount of antibody transfer
- Other indications
- Primary series: 3 doses (0, 1, 7 months), in any combination of Tdap or Td, with at least 1 dose of Tdap
- Booster: 1 dose (either Td or Tdap) every 10 years, especially for HCP or elderly
- SVL
- Boostrix
- Adacel
- Only applicable during pregnancy
- Tdap + Polio (IPV)
- Boostrix-Polio
- Adacel-Polio
- NCIS routine schedule
- 1 dose at 10-11 years old
- Labelled as "B2" on chart
- SVL
- Boostrix-Polio
- Adacel-Polio
- 5-in-1
- Infanrix-IPV+HiB
- Pentaxim
- 6-in-1
- Infanrix Hexa
- Hexaxim
- Universal
- 5-in-1
- 2 months onwards
- Upper age limit:
- Infanrix-IPV+HiB : < 5 years old
- Pentaxim : not stated
- 6-in-1
- 6 weeks onwards
- Upper age limit:
- Infanrix Hexa : not stated
- Hexaxim : < 2 years old
- NCIS
- Routine schedule
- 2 months (D1): 6-in-1
- 4 months (D2): 5-in-1
- 6 months (D3): 6-in-1
- 18 months (B1): 5-in-1
- Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers
- 2 months (D1): 5-in-1
- 4 months (D2): 5-in-1
- 6 months (D3): 6-in-1
- 18 months (B1): 5-in-1
- SVL
- Infanrix-IPV+HiB
- Infanrix Hexa
- Pentaxim
- Hexaxim
- BCG
- BCG AJV (LIVE)
- Intradermal
- < 1 yo: 0.05 ml
- 1 yo and older: 0.1 ml
- 1 dose
- Given at birth
- Up to 90% protection against TB meningitis and miliary TB if given in neonatal period
- Vaccinated children ~ 19% less likely to be infected with TB compared to unvaccinated children
- 2 years and up
- Travellers to endemic areas
- Migrants
- Healthcare professionals
- Military personnel
- Mandatory vaccination for food handlers ceased since September 2010
- 1 dose
- Booster every 2-3 years if risk persists
- Cholera
- Dukoral (inactivated)
- PO
- Prepare sodium hydrogen carbonate buffer solution (dissolve effervescent granules in 150 ml of cool water)
- 2 to 6 yo: pour away half (75 ml) of buffer solution
- Mix vaccine (suspension) into buffer solution and consume within 2 hours
- 2 years and up
- Travellers to endemic / epidemic areas
- 2 to 6 years
- 3 doses, 1 to 6 weeks apart
- 1 booster dose after 6 months
- 7 years and up
- 2 doses, 1 to 6 weeks apart
- 1 booster dose after 2 years
- Notes for all ages
- Last dose to be completed at least 1 week before trip
- If interval between doses exceed 6 weeks, to restart schedule
- Rotavirus
- Rotarix (LIVE)
- PO
- 1.5 ml
- Oral applicator syringe or tube form
- RotaTeq (LIVE)
- Both brands: administer towards inner cheek with child seated and leaning back slightly
- 6 weeks to 24 weeks (Rotarix) / 32 weeks (RotaTeq)
- Universal (but not in NCIS)
- Contraindicated in:
- History of intussusception
- Uncorrected congenital malformation of GI tract that may predispose to intussusception (e.g. Meckel’s diverticulum)
- Rotarix
- 2 doses
- 4 weeks apart
- Start preferably by 16 weeks, but latest by 20 weeks
- 2nd dose no later than 24 weeks
- RotaTeq
- 3 doses
- 4 weeks apart
- Start between 6 to 12 weeks
- 3rd dose no later than 32 weeks
- Meningococcal
- ACWY (conjugate)
- Nimenrix
- MenQuadfi
- Menveo
- Menactra
- B (recombinant protein)
- Trumenba
- Haj requirements
- Visa requirement for travellers 1 year and older
- 1 dose of quadrivalent (ACWY) vaccine at least 10 days prior to arrival
- Conjugate vaccine valid for 5 years
- Polysaccharide vaccine (not available in Singapore) valid for 3 years
- Nimenrix
- Primary vaccination
- 6 weeks to 5 months: 2 doses, 2 months apart + 1 booster at 12 months
- 6 months to 11 months: 1 dose + 1 booster at 12 months (and at least 2 months after previous dose)
- 12 months and older: 1 dose
- Booster
- 15 to 55 years: 1 dose if at least 4 years since last dose
- MenQuadfi
- 1 year and older: 1 dose
- Booster can be given, but no manufacturer recommendation for timing/indication
- Menveo
- Primary vaccination
- 2 to 6 months: 3 doses, 2 months apart; 4th dose at 12 to 16 months
- 7 to 23 months: 2 doses with 2nd dose on or after 12 months, and at least 2 months after 1st dose
- 2 to 65 years: 1 dose
- Booster
- Booster can be given, but no manufacturer recommendation for timing/indication
- Menactra
- Primary vaccination
- 9 to 23 months: 2 doses, 3 months apart
- 2 to 55 years: 1 dose
- Booster
- 15 to 55 years: 1 dose if at least 4 years since last dose
- COVID-19
- mRNA vaccines
- Pfizer (Comirnaty)
- IM
- 0.3 ml
- each age range has own type of single-dose vial
- Moderna (Spikevax)
- Protein subunit vaccine
- Novavax (Nuvaxovid)
- IM
- 0.5 ml
- currently unavailable in SG
- MOH Circular 67/2025 (24 October 2025)
- Recommended for vaccination (either initial doses or booster doses) in 2025/2026:
- 60 years and above
- 6 months and above if medically vulnerable
- Residents of aged care facilities
- Encouraged for vaccination:
- Healthcare workers
- Persons living or working with medically vulnerable individuals
- Others aged 6 months and above who wish to be vaccinated can continue to do so
- Primary vaccination
- 6 months to 4 years
- Pfizer: 2 doses (3 mcg each), 21 days to 8 weeks apart
- Moderna: 2 doses (25 mcg each), 28 days to 8 weeks apart
- 5 to 11 years
- Pfizer: 1 dose (10 mcg)
- Moderna: 1 dose (25 mcg)
- 12 years and above
- Pfizer: 1 dose (30 mcg)
- Moderna: 1 dose (50 mcg)
- Novavax: 1 dose (5 mcg)
- Immunocompromised
- 3 doses in total, regardless of age
- 6 months to 4 years: add D3 2 months after D2
- 5 years and above: 0, 2, 4 months
- Booster doses
- 1 dose ~ 1 year from last dose
- Minimum interval of 5 months
- Brand and dosage according to age groups as above
- Recently recovered from COVID-19
- Wait at least 4 weeks after infection
- But 3 months is better for greater effectiveness
- Free under the National Vaccination Programme (NVP) for all Singapore Citizens, Permanent Residents, Long Term Pass Holders and certain Short Term Pass holders